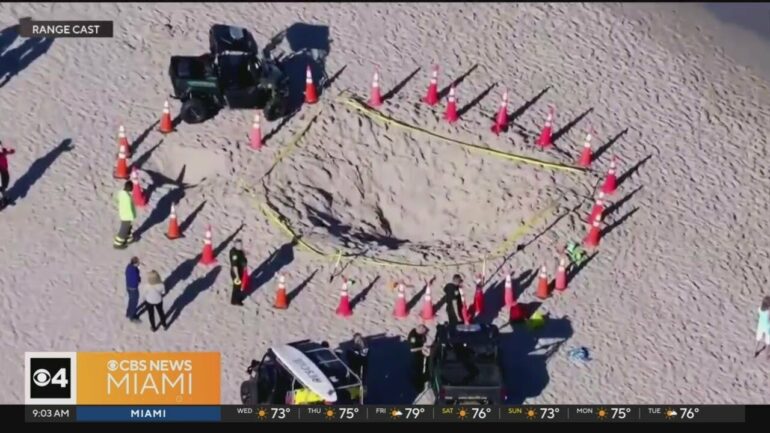
While millions of Americans vacation on beaches every year to seek out sun, sand and the sea, many might not realize how dangerous digging holes in the sand can be. In February 2024, a 7-year-old girl died after an approximately 5-foot (1.5-meter) hole she and her brother dug in the sand collapsed in on her, burying her alive.
As a coastal science researcher who’s been studying beaches for many years, I was called in to help investigate the girl’s death. While many people nearby stepped in to try to free the girl after the sand hole collapsed, local firefighters couldn’t arrive until several minutes after the incident – too late to resuscitate the victim.
A young girl suffocated in Lauderdale-by-the-Sea, Fla., after a sand hole collapsed on her in February.
Digging holes in sand might seem innocent, but if the hole is deep enough and collapses on a person, it is extremely difficult to escape. In fact, research suggests more people die from sand burial suffocation than from shark attacks.
Sand basics
Sand isn’t actually a type of material. It’s a category of material size, ranging from 0.0025 to 0.08 inches (0.06 to 2 millimeters) in diameter. The type of sand is determined by the materials making it up. Quartz sand, made up of silicon dioxide, is the most common sand found on beaches, except at tropical coasts where coral sand beaches, made up of calcium carbonate, are found.
Material coarser than sand is not soft to the touch – it doesn’t make sturdy sandcastles. Silt and clay, which are finer than sand, make water murky and are commonly called mud.
Sand’s weight depends on the materials it’s made of. Pure quartz sand beaches, which have very white sand, weigh around 90 pounds per cubic foot when dry.
But most beaches contain a mixture of minerals, creating a tan or brown appearance. The minerals that darken the sand are much heavier – sand on most beaches would weigh up to 130 pounds per cubic foot when dry.
Dry, loose grains of sand will form a pile with a slope angle of about 33 degrees, termed its angle of repose. The angle of repose is the steepest angle at which a pile of grains remains stable, and the force of friction between each grain determines that stability.

The angle of repose describes the slope of a pile of sand.
Davius/Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA
Sand is more stable when it’s wet because the surface tension between water and sand grains can hold the pile of sand in place vertically. But once it dries, the pile will collapse, as there’s no more surface tension.
So if you dig a hole in the beach, it’ll stay stable for as long as the sand stays moist. Once it dries, the hole collapses.
Sand is unstable
When either the sand forming the hole dries out or someone stands near the edge of the hole, adding extra weight, the sand hole collapses in, and the heavy grains fill all…