It’s rare to attend an outdoor party in warm weather without hearing people complain about mosquitoes. They swat away, sit in campfire smoke, cover up with blankets and eventually just give up and go indoors. On the other end of the spectrum, there are plenty of people who don’t seem bothered by mosquitoes in the slightest.
As a medical entomologist who’s worked with mosquitoes for more than 40 years, I’m often asked why some people seem to be mosquito magnets while others are oblivious to these blood-feeding pests buzzing all around them.
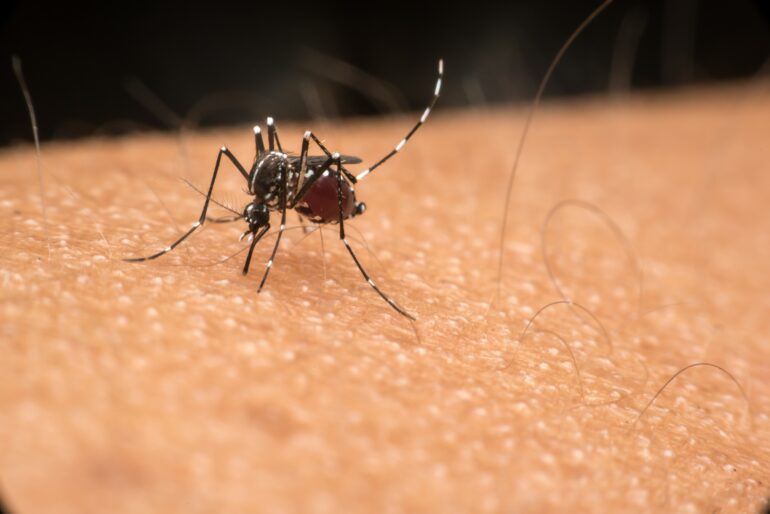
Most mosquito species, along with a host of other arthropods – including ticks, fleas, bedbugs, blackflies, horseflies and biting midges – require the protein in blood to develop a batch of eggs. Only the female mosquito feeds on blood. Males feed on plant nectar, which they convert to energy for flight.
Blood-feeding is an incredibly important part of the mosquito’s reproductive cycle. Because of this, a tremendous amount of evolutionary pressure has been placed on female mosquitoes to identify potential sources of blood, quickly and efficiently get a full blood meal, and then stealthily depart the unlucky victim. If you check some, or all, of the mosquito’s search boxes, then you may find that you are a mosquito magnet.
This video by Deep Look explains some of the ways mosquitoes feed on blood.
Sensing CO2 and scent signals
Depending on when during the day they are active, mosquitoes use sight, sound and olfactory cues to identify a potential source of blood. Most night-active species rely on olfactory or receptor cues. The most important chemical cue is the carbon dioxide that all vertebrates, including humans, release with each breath and through their skin.
Mosquitoes are very sensitive to CO2 and can sense a CO2 source that is many meters away. Receptor cells on the mosquito’s antennae and legs bind CO2 molecules and send an electrical signal to the brain. When more molecules hit their receptors, the higher the CO2 concentration and the closer they are to the host.
However, there are many nonliving carbon dioxide sources such as cars, boats, planes and trains. To separate living from nonliving sources of CO2, mosquitoes rely on the secondary olfactory cues that living animals produce. Metabolic processes like breathing and moving generate these scent cues, including lactic acid, ammonia and fatty acids that act as additional olfactory clues that help female mosquitoes zero in on their next blood meal.
So, carbon dioxide production is the first mark of a mosquito magnet. Because the production of CO2 and secondary attractants is linked to metabolic rate, the higher the metabolic rate, the more attractants are produced. Metabolic rate can be genetically determined, but it also increases as the result of physical activity.
The human mosquito magnets you can spot at summer parties may have a genetically…