The U.S. Internal Revenue Service is planning to require citizens to create accounts with a private facial recognition company in order to file taxes online. The IRS is joining a growing number of federal and state agencies that have contracted with ID.me to authenticate the identities of people accessing services.
The IRS’s move is aimed at cutting down on identity theft, a crime that affects millions of Americans. The IRS, in particular, has reported a number of tax filings from people claiming to be others, and fraud in many of the programs that were administered as part of the American Relief Plan has been a major concern to the government.
The IRS decision has prompted a backlash, in part over concerns about requiring citizens to use facial recognition technology and in part over difficulties some people have had in using the system, particularly with some state agencies that provide unemployment benefits. The reaction has prompted the IRS to revisit its decision.
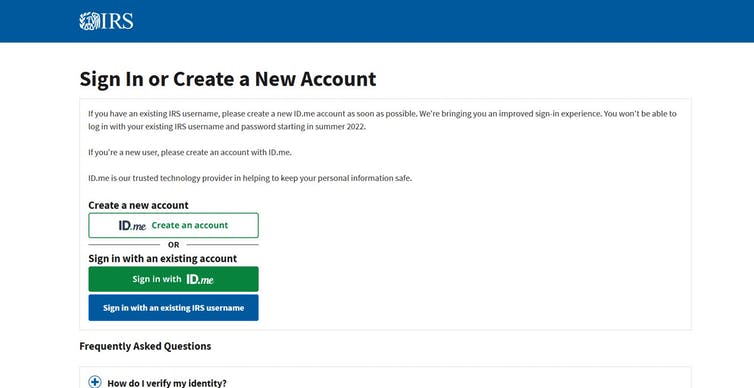
Here’s what greets you when you click the link to sign into your IRS account. If current plans remain in place, the blue button will go away in the summer of 2022.
Screenshot, IRS sign-in webpage
As a computer science researcher and the chair of the Global Technology Policy Council of the Association for Computing Machinery, I have been involved in exploring some of the issues with government use of facial recognition technology, both its use and its potential flaws. There have been a great number of concerns raised over the general use of this technology in policing and other government functions, often focused on whether the accuracy of these algorithms can have discriminatory affects. In the case of ID.me, there are other issues involved as well.
ID dot who?
ID.me is a private company that formed as TroopSwap, a site that offered retail discounts to members of the armed forces. As part of that effort, the company created an ID service so that military staff who qualified for discounts at various companies could prove they were, indeed, service members. In 2013, the company renamed itself ID.me and started to market its ID service more broadly. The U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs began using the technology in 2016, the company’s first government use.
To use ID.me, a user loads a mobile phone app and takes a selfie – a photo of their own face. ID.me then compares that image to various IDs that it obtains either through open records or through information that applicants provide through the app. If it finds a match, it creates an account and uses image recognition for ID. If it cannot perform a match, users can contact a “trusted referee” and have a video call to fix the problem.
A number of companies and states have been using ID.me for several years. News reports have documented problems people have had with ID.me failing to authenticate them, and with the company’s customer support in resolving those…