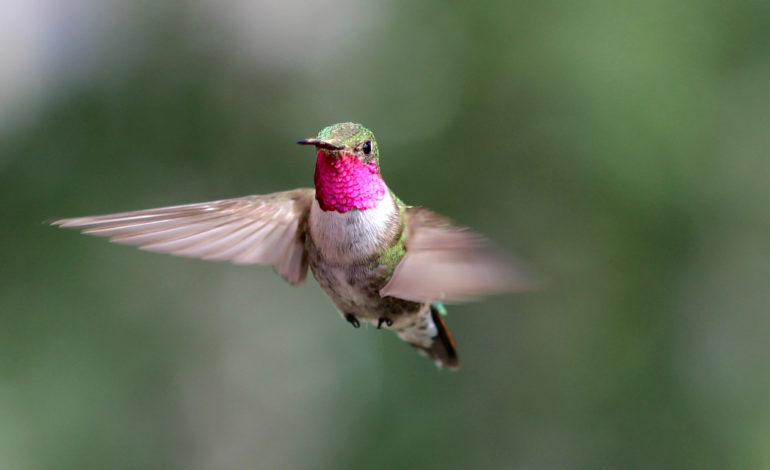
To find food, dazzle mates, escape predators and navigate diverse terrain, birds rely on their excellent color vision.
“Humans are color-blind compared to birds and many other animals,” said Mary Caswell Stoddard, an assistant professor in the Princeton University Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology. Humans have three types of color-sensitive cones in their eyes—attuned to red, green and blue light—but birds have a fourth type, sensitive to ultraviolet light. “Not only does having a fourth color cone type extend the range of bird-visible colors into the UV, it potentially allows birds to perceive combination colors like ultraviolet+green and ultraviolet+red—but this has been hard to test,” said Stoddard.
To investigate how birds perceive their colorful world, Stoddard and her research team established a new field system for exploring bird color vision in a natural setting. Working at the Rocky Mountain Biological Laboratory (RMBL) in Gothic, Colorado, the researchers trained wild broad-tailed hummingbirds (Selasphorus platycercus) to participate in color vision experiments.
“Most detailed perceptual experiments on birds are performed in the lab, but we risk missing the bigger picture of how birds really use color vision in their daily lives,” Stoddard said. “Hummingbirds are perfect for studying color vision in the wild. These sugar fiends have evolved to respond to flower colors that advertise a nectar reward, so they can learn color associations rapidly and with little training.”
Stoddard’s team was particularly interested…