When it comes to efficiency and quality, light-emitting diodes (LED) are the MVP of today’s lighting technology. A team of Chinese researchers are using recent LED improvements as a springboard to launch a more interconnected illumination network.
In their study published on September 30, 2022 in Intelligent and Converged Networks, they proposed the concept of an Internet of Light that interfaces with the Internet of Things to improve human health and well-being by providing information services.
“As people spend more and more time indoors, it is absolutely necessary to provide an illumination network that offers intelligent lighting along with information services by combining information technologies with communication technologies,” said Jian Song, Tsinghua University professor of electronic engineering.
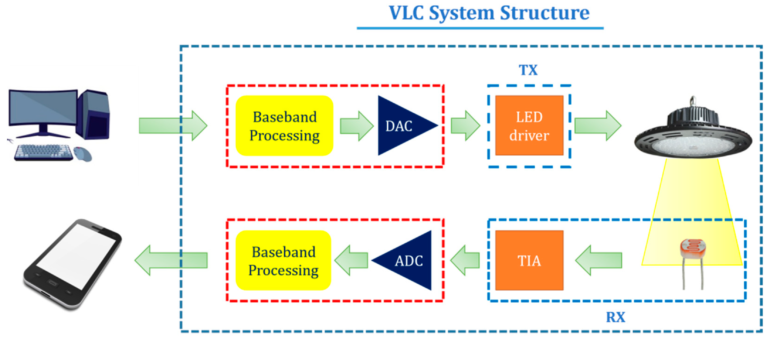
Since LED is silicon-based, it can facilitate deep integration of illumination networks with different electronic and intelligent control mechanisms at low cost. On top of illumination control, researchers from information and communication technology (ICT) areas have demonstrated the feasibility of something called visible light communication (VLC), which transmits information by modulating LED light intensity. This form of communication could simultaneously support information services such as localization, data transmission and even optical therapy without causing eyestrain or damage.
“The rapid progress in the related areas of ICT and human science motivated us to propose the idea of Internet of Light (IoL) as a platform and develop its key functionalities,” Song said.
To integrate IoL with ubiquitous illumination networks, the researchers combined sensors, communication modules and smart processing units into individual LED lamps to form a “node,” and adopted telecommunication technologies, such as powerline communications (PLC) and 5G wireless communications as the means of networking.
An IoL sensor network comprised of specially designed sensing nodes can collect information such as light intensity, color, the level of hazardous gas, moving objects and more.
Applications of this type of IoL include “smart” nursing homes where a resident can be located for safety and security reasons or a kitchen gas leakage can be detected in time. Automatic adjustments in light intensity or color can customize a comfortable environment according to user preference or as a means to conduct optical therapy.
To accommodate these functionalities effectively and efficiently, the researchers developed algorithms and conducted hardware experiments to demonstrate system performance for high-speed data delivery. This included experimenting with real-time beam alignment VLC design that can swiftly adjust the direction of the emitting light source according to the user’s position.
The researchers investigated resource optimization under different constraints such as communication and location services to allocate different frequencies and power, as well as communication and illumination to meet a variety of illumination requirements including intensity and uniformity.
“As both communication and position services will be carried out by the illumination networks, optimization of power allocation is critical,” said Hui Yang, Tsinghua University professor of electronic engineering.
To support applications such as video transmission and real-time positioning, researchers are exploring scheduling algorithms that can accommodate a base station’s stringent timing requirements and minimize latency.
Previous studies demonstrated that light can be used to treat certain dermatoses or neurodegenerative diseases, showing the possibility for non-intrusive optical treatment. The team explored this possibility by designing an experiment of light stroboscopic irradiation with flicker frequency of LED light.
“The preliminary results of our investigation confirmed the relationship between light stimulation and human reaction by electrodermal activity signal and other methods,” said Xiaofei Wang, Tsinghua University professor of electronic engineering. “This demonstrates that an IoL platform can possibly regulate human emotions and brain activity by controlling the flicker frequency of the light source intelligently and automatically.”
In future steps, the researchers plan to integrate individual technologies into an environment like a nursing facility, which could benefit from smart sensing, communications and optimization under resource constraints, according to the study.
The combination of lighting and environment creates a highly interactive, complex and dynamic system with huge discrepancy and great diversity for individual people,” said Luoxi Hao, professor in the Tongji University College of Architecture and Urban Planning. “The advantages of real-time perception, instantaneous response and seamless information interconnection supported by IoL can surely play an important role in bringing a human-centric lighting concept into reality.”
More information:
Jian Song et al, Internet of light: Technologies and applications, Intelligent and Converged Networks (2022). DOI: 10.23919/ICN.2022.0018
The paper is also available on SciOpen (www.sciopen.com/article/10.23919/ICN.2022.0018) by Tsinghua University Press.
Provided by
Tsinghua University Press
Citation:
‘Internet of Light’ integrates illumination, communication and ministration (2023, January 13)