Whenever I teach about memory in my child development class at Rutgers University, I open by asking my students to recall their very first memories. Some students talk about their first day of pre-K; others talk about a time when they got hurt or upset; some cite the day their younger sibling was born.
Despite vast differences in the details, these memories do have a couple of things in common: They’re all autobiographical, or memories of significant experiences in a person’s life, and they typically didn’t happen before the age of 2 or 3. In fact, most people can’t remember events from the first few years of their lives – a phenomenon researchers have dubbed infantile amnesia. But why can’t we remember the things that happened to us when we were infants? Does memory start to work only at a certain age?
Here’s what researchers know about babies and memory.
Infants can form memories
Despite the fact that people can’t remember much before the age of 2 or 3, research suggests that infants can form memories – just not the kinds of memories you tell about yourself. Within the first few days of life, infants can recall their own mother’s face and distinguish it from the face of a stranger. A few months later, infants can demonstrate that they remember lots of familiar faces by smiling most at the ones they see most often.
In fact, there are lots of different kinds of memories besides those that are autobiographical. There are semantic memories, or memories of facts, like the names for different varieties of apples, or the capital of your home state. There are also procedural memories, or memories for how to perform an action, like opening your front door or driving a car.
Research from psychologist Carolyn Rovee-Collier’s lab in the 1980s and 1990s famously showed that infants can form some of these other kinds of memories from an early age. Of course, infants can’t exactly tell you what they remember. So the key to Rovee-Collier’s research was devising a task that was sensitive to babies’ rapidly changing bodies and abilities in order to assess their memories over a long period.
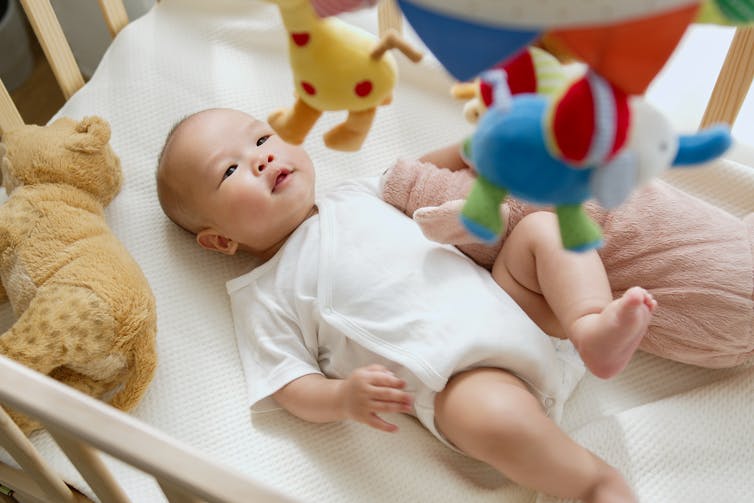

A mobile in motion can keep a baby entertained.
Nattakorn Maneerat/iStock via Getty Images
In the version for 2- to 6-month-old infants, researchers place an infant in a crib with a mobile hanging overhead. They measure how much the baby kicks to get an idea of their natural propensity to move their legs. Next, they tie a string from the baby’s leg to the end of the mobile, so that whenever the baby kicks, the mobile moves. As you might imagine, infants quickly learn that they’re in control – they like seeing the mobile move and so they kick more than before the string was attached to their leg, showing they’ve learned that kicking makes the mobile move.
The version for 6- to 18-month-old infants is similar. But instead of lying in a crib – which this age group just won’t do for…