Buying drugs on the street is a game of Russian roulette. From Xanax to cocaine, drugs or counterfeit pills purchased in nonmedical settings may contain life-threatening amounts of fentanyl.
Physicians like me have seen a rise in unintentional fentanyl use from people buying prescription opioids and other drugs laced, or adulterated, with fentanyl. Heroin users in my community in Massachusetts came to realize that fentanyl had entered the drug supply when overdose numbers exploded. In 2016, my colleagues and I found that patients who came to the emergency department reporting a heroin overdose often only had fentanyl present in their drug test results.
As the Chief of Medical Toxicology at UMass Chan Medical School, I have studied fentanyl and its analogs for years. As fentanyl has become ubiquitous across the U.S., it has transformed the illicit drug market and raised the risk of overdose.
Fentanyl and its analogs
Fentanyl is a synthetic opioid that was originally developed as an analgesic – or painkiller – for surgery. It has a specific chemical structure with multiple areas that can be modified, often illicitly, to form related compounds with marked differences in potency.
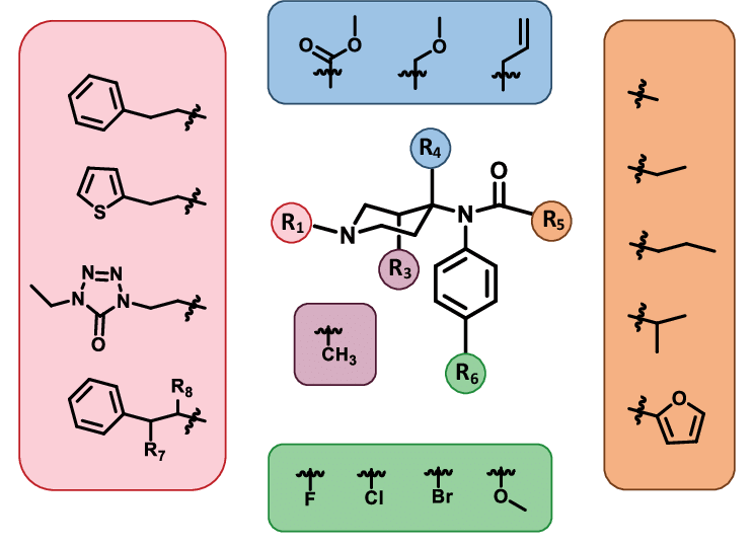
Fentanyl’s chemical backbone (the structure in the center) has multiple areas (the colored circles) that can be substituted with different functional groups (the colored boxes around the edges) to change its potency.
Christopher Ellis et al., CC BY-NC-ND
For example, carfentanil, a fentanyl analog formed by substituting one chemical group for another, is 100 times more potent than its parent structure. Another analog, acetylfentanyl, is approximately three times less potent than fentanyl, but has still led to clusters of overdoses in several states.
Despite the number and diversity of its analogs, fentanyl itself continues to dominate the illicit opioid supply. Milligram per milligram, fentanyl is roughly 50 times more potent than heroin and 100 times more potent than morphine.
Lacing or replacing drugs with fentanyl
Drug dealers have used fentanyl analogs as an adulterant in illicit drug supplies since 1979, with fentanyl-related overdoses clustered in individual cities.
The modern epidemic of fentanyl adulteration is far broader in its geographic distribution, production and number of deaths. Overdose deaths roughly quadrupled, going from 8,050 in 1999 to 33,091 in 2015. From May 2020 to April 2021, more than 100,000 Americans died from a drug overdose, with over 64% of these deaths due to synthetic opioids like fentanyl and its analogs.
Illicitly manufactured fentanyl is internationally synthesized in China, Mexico and India, then exported to the United States as powder or pressed pills. Additionally, the emergence of the dark web, an encrypted and anonymous corner of the internet that’s a haven for criminal activity, has facilitated the sale of fentanyl and other opioids shipped through traditional…